Valerian Complex is a supplement promoting sleep and relaxation that contains Valerian root, Passion Flower and Jujube seed.*
These herbs have been traditionally used in herbal preparations to:
- Relieve mild nervous tension*
- Obtain relief from occasional sleeplessness*
- Promote relaxation*
- Ease the effects of temporary or occasional stress*
This combination of herbs contains many compounds including iridoids (known as valepotriates), an essential oil, cyclopentane sesquiterpenes (including valerenic acid), flavonoids and dammarane-type saponins called jujubosides.
Valerian Quality Story
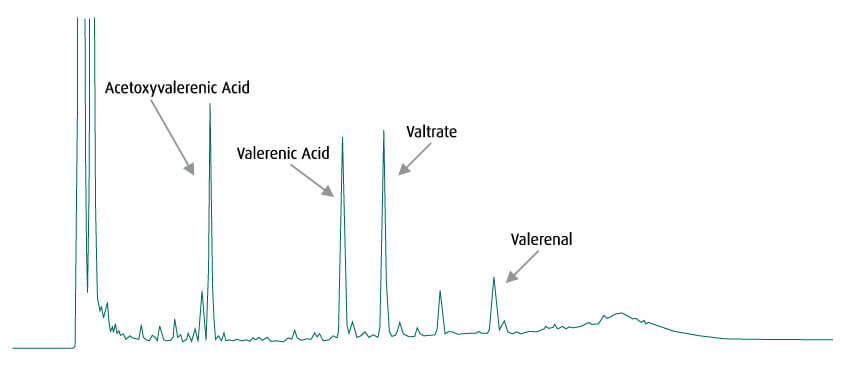
Valerian (Valeriana officinalis) contains valerenic acids (predominantly acetoxyvalerenic and valerenic acid and low levels of hydroxyvalerenic acid) and valepotriates (valtrate and isovaltrate). While other species of Valerian may contain the valepotriates only true Valerian contains the valerenic acids. MediHerb has developed a unique HPLC analytical method to determine the levels of valerenic acids and valepotriates in Valerian. This method can also determine the level of the baldrinals (valtrate degradation products) which are an indicator of a poor quality herb. By using this analytical method on all its Valerian products, MediHerb ensures that these products contain high levels of valerenic acids and valepotriates, with no baldrinals.
Passion Flower Quality Story
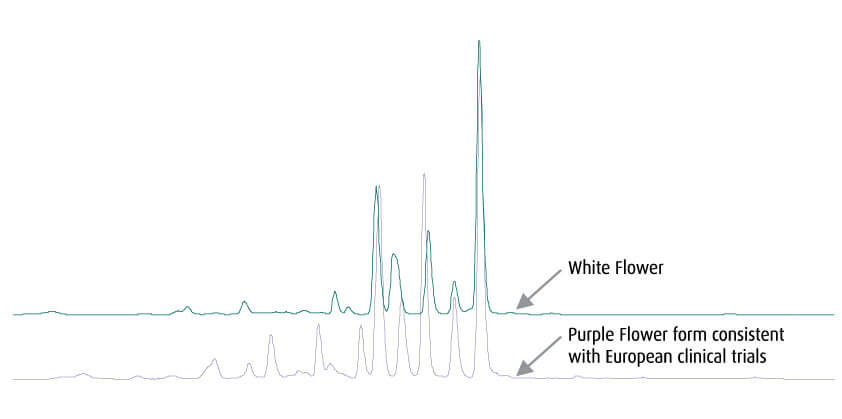
There are over 500 species of Passion Flower, which include the edible passionfruit and varieties grown for their characteristic flowers. The preferred medicinal species is Passiflora incarnata which is native to the Americas and has many common names, including ‘Maypop’ and ‘Purple Passion Flower’. The original forms of this plant have flowers varying in color from pale lavender through to dark violet. There is also a white-flowered form which appears in the wild, as well as in cultivation, and is sold as P. incarnata “Alba”.
During routine analysis in the MediHerb Research Laboratory it became evident that there were two different phytochemical profiles of Passion Flower being encountered. The samples varied in the flavonoid constituents which are among the proposed clinically active components. In conjunction with Southern Cross University (Australia) it was determined that the different flavonoid profiles were related to the color of the flowers (purple or white). The clinical evidence for Passion Flower is derived from European clinical trials and the corresponding phytochemical profiles have been published. By using LC/MS it was determined that these profiles matched that of the purple-flowered form. Two of the peaks are consistent between the two different forms, however, the remaining eight or more flavonoids are different. Without using at least HPLC, or ideally LC/MS, this differentiation is easily missed and the inappropriate form of Passiflora incarnata might be used. Our analysis ensures that the Passion Flower in MediHerb products is the appropriate form.