Page 77 - 2018 SP Product Guide
P. 77
Wild Yam
Quality Story
There are some 600 species of Yam in the genus Dioscorea, Commercially available Dioscorea villosa is in the form of dried roots,
many of them are wild species that flourish in damp usually harvested at the end of summer or fall when the plant is dying
woodlands and thickets. Dioscorea villosa, also known as Colic back to its rootstock. It was found that these roots contained only very
Root or Wild Yam, is a twining, tuberous vine native to eastern small amounts of dioscin, not the predominance as previously thought.
North America. The major saponin found in the fall harvested roots were in fact the
furostanol-based saponins, methylparvifloside and methylprotodeltonin,
The roots initially taste starchy, but soon after are bitter and acrid, nothing while the spirostanol-based saponins, Zingiberensis saponin I and
like the taste of Yam or Sweet Potato grown for the dinner table. deltonin were the major saponins for samples harvested in summer. The
Commercial Wild Yam extracts available for use as raw materials are storage saponins from the fall differ from the summer saponins by the
often not Dioscorea villosa but instead Dioscorea opposita (Chinese Yam presence of an extra glucose at the C-26 position of the diosgenin base
Root) which has a different phytochemical profile. structure. The two main compounds found in commercial material –
It is widely misconstrued that Dioscorea villosa contains diosgenin and harvested in the fall – are significantly different from dioscin by having an
many products have this as a statement on their labels. However it does extra one or two glucose residues in methylprotodeltonin and
not contain diosgenin, but rather the diosgenin precursors. Traditionally methylparvifloside respectively. All of these compounds have been
Dioscorea villosa was believed to contain predominantly dioscin, reported from other Disocorea species, however, the profile of saponins
however, the origin of this assignment is unclear (dioscin is a steroidal was different in the other species.
glycoside precursor of diosgenin). The phytochemical profile of Wild Yam
is poorly-defined and based on scientific literature from the 1940s.
®
MediHerb undertook a project in conjunction with Associate Professor
James De Voss, Chemistry Department, from the University of
Queensland, Australia to investigate the phytochemistry.
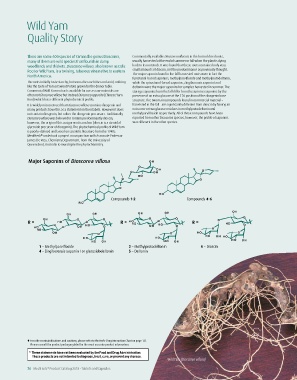
Major Saponins of Dioscorea villosa
Compounds 1-2 Compounds 4-6
R = R = R =
1 – Methylparvifloside 2 – Methylprotodeltonin 6 – Dioscin
4 – Zingiberensis saponin I or glucosidodeltonin 5 – Deltonin
tFor other contraindications and cautions, please refer to the Herb-Drug Interaction Chart on page 131.
Please consult the product packaging label for the most accurate product information.
* These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.
These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Wild Yam (Dioscorea villosa)
76 MediHerb Product Catalog 2018 • Tablets and Capsules
®